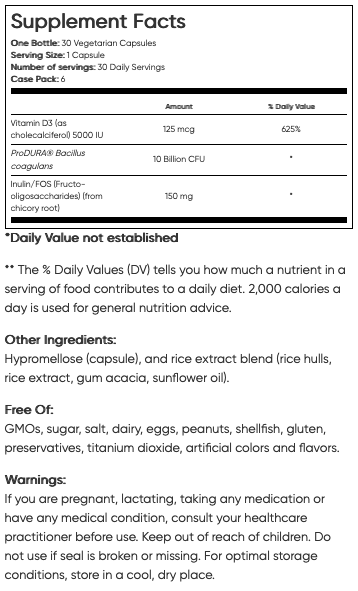
Discover the Health Benefits of Vitamin D3 + Probiotics
Vitamin D can be attained through two sources: UVB light and diet. When exposed to sunlight, the body manufactures vitamin D from cholesterol, this is where Vitamin D draws its nickname, “the sunshine vitamin. Still, some people do not make enough vitamin D from the sun, among them, people who have a darker skin tone, who are overweight, who are older, and who cover up when they are in the sun.
According to experts, the gold standard in Vitamin D supplementation is D3, also known as cholecalciferol. The reaction that takes place from exposure to UVB light results in the formation of Vitamin D3; for this reason, D3 is known as the natural form of Vitamin D. UV radiation is a known human carcinogen, making supplementation a safer alternative to achieving optimal Vitamin D levels.
Probiotics are live nonpathogenic microorganisms that are introduced into the digestive tract to improve microbial balance. Prebiotics and Probiotics have been shown to have the ability to manipulate the microbial composition and support healthy immune response of an individual.
Scientific Support
Immune health and digestive health are interconnected and both can be supported by Vitamin D3 with Probiotics. Combined, these nutrients promote the symbiotic balance of the immune system while promoting digestive, cardiovascular, and musculoskeletal health. Western diets have grown increasingly poor in the past decades, resulting in higher intakes of processed and sugar-laden foods and a decrease in fiber intake. Simultaneously we have seen an increase in inflammatory disease processes making it reasonable to suggest that diet and poor health are related. Vitamin D3 and probiotics both play a clear role in improving digestion and addressing inflammation and can be influenced by dietary choices.
- Vitamin D has been shown to have a role in the immune system by regulating antimicrobial protein levels and influencing infection control.
- Bacillus coagulans has shown promising benefits for irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), diarrhea, gas, respiratory infection, and immune function.
- B. coagulans are better able to survive in high-temperature heat treatment and stomach conditions than other commercial probiotic microorganisms.
- An analysis of 12 fracture prevention trials that included more than 40,000 elderly people, most of them women, found that intakes of at least 800IU of Vitamin D daily reduced hip and non-spine fractures by 20 percent, while lower intakes failed to offer any fracture prevention benefit.
- Individuals who are deficient in Vitamin D are twice as likely to suffer from a heart attack when compared to those who have adequate levels
- Low Vitamin D levels have been correlated to a higher risk of heart failure, sudden cardiac death, stroke, overall cardiovascular disease, and cardiovascular death.
- Research suggests that Vitamin D protects individuals from cardiovascular disease by playing a role in blood pressure regulation, which subsequently prevents artery damage, a key factor in cardiovascular disease and related decline. One study found that improving the Vitamin D status of a hypertensive patient led to a drop of systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
- Diet alone has the strongest and most direct impact on gut microbial colonization. Dietary consumption of prebiotics and probiotics has the ability to induce major shifts in gut microbial composition, directly affecting the mucosal immune system and resulting in positive effects on enteric inflammatory disorders and the systemic immune response.
- Bacteria that inhabit the gut regulate the colonization and eradication of pathogens. Thus, the administration of oral probiotics and prebiotics that boost the growth of natural competitors should be an effective treatment of enteric diseases.
† These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration.
This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.